japanese beetle life cycle ontario
They are in different stages during their life cycle. However most of the damage to ornamentals and turf grass happens during the spring and fall the second year.

Pin On Bugs The Good The Bad For Fun
During the summer feeding period females intermittently leave plants burrow about 3 inches into the groundusually into lawnsand lay a few eggs.

. In cultivated soils this may be deeper. Orkin Termite Treatment Pest Control Exterminator Service. Lack of snow cover may increase larval mortality.
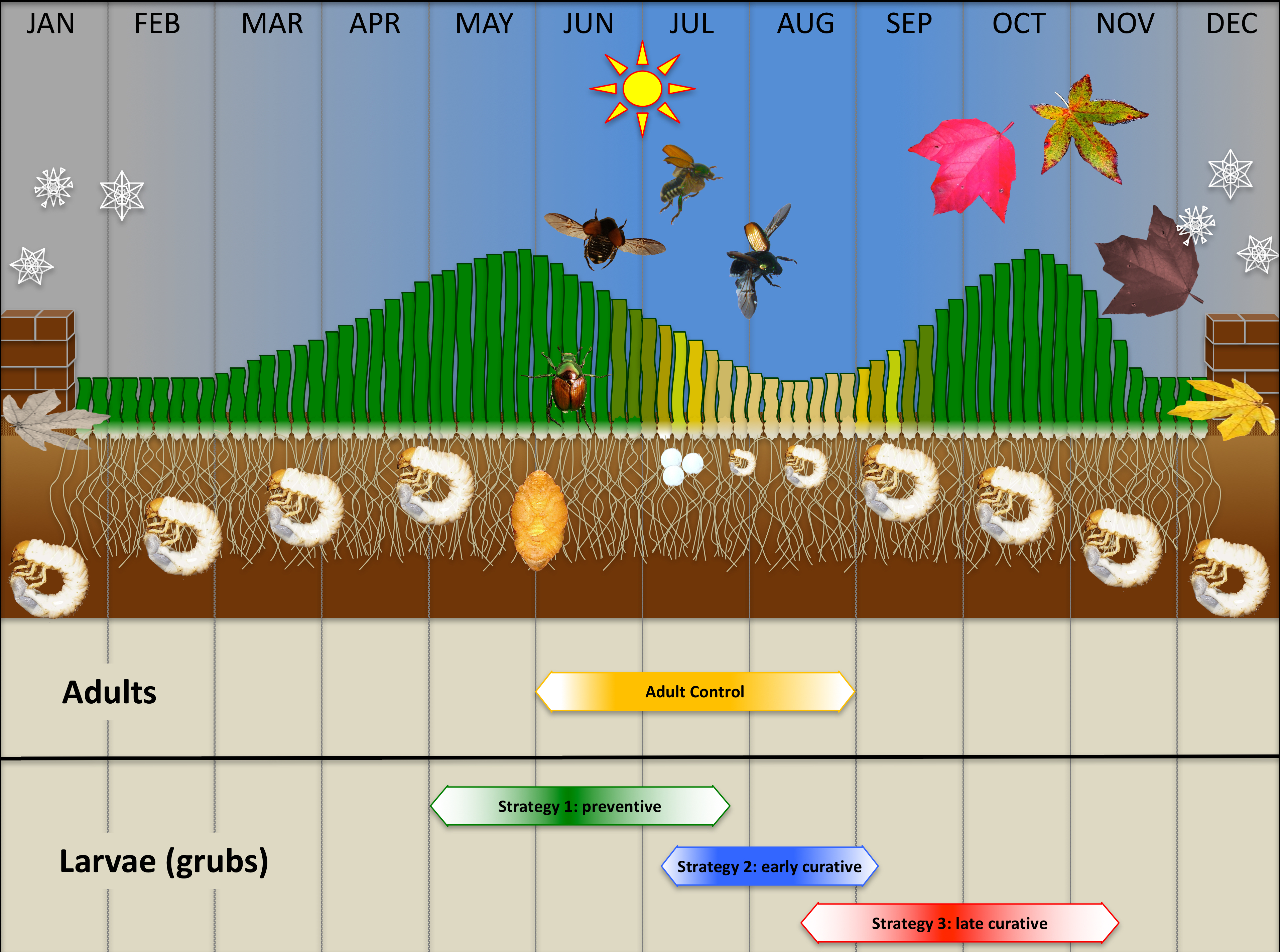
In September as soils begin to cool grubs move deeper into the soil and remain where the soil is about 10C at a depth of about 15-25 cm. This is when grubs are present in the top inch of the root zone heavily feeding on grass roots and thatch. For JB our registered soil-applied pesticides are going to have much less effect against the pupal and egg stages.
When temperatures exceed 35 C and relative humidity is greater than 60 flight ceases. Adult June bugs lay 75 to 100 eggs underground in early to midsummer. Applying nematodes in the spring and fall when they live in your soil as grubs can kill the problem before they emerge as adult beetles.
The beetle only appears in midsummer and is active for six to eight weeks before laying a batch of eggs in lawns or grassy areas. This is called the first instar. The pupae stage is where the grub starts to transform into a beetle.
Most of the beetles life is spent as a larva with only 3045 days spent as an imago. Their normal life span is from 30 to 45 days. Their normal life span is from 30 to 45 days.
Japanese beetle pupae start as cream-colored and age to a reddish-brown. Only the nematode heterorhabditis bacteriophora is effective in Japanese beetle grub control. The immature stage of the Japanese beetle the white grub typically has a three year life cycle.
Applying nematodes in the spring and fall when they live in your soil as grubs can kill the problem before they emerge as adult beetles. Look for these shiny green and copper beetles feeding on grape leaves roses and many other trees and shrubs. When the egg hatches the newly emerged larva feeds upon the inner tissues of the tree and branch trunks in the vicinity.
Image by Joel Floyd USDA-APHIS-PPQ. Mid summer rains keep these alive in dry years they will die off. If you see parasitized Japanese beetles it is important to leave them in the wild so that this predator can continue its life cycle.
If you see a white dot on the head of a beetle it. After about 18 days larvae emerge from the eggs. A temperature of 21C and a relative humidity of 60 are ideal for beetle flight.
These hatch and the small larvae begin feeding on grassroots and. OMAFRA Factsheet Japanese Beetles in Nursery and Turf Japanese Beetle Life Cycle Beetles emerge from the soil in late June or early July begin flying when the temperature is about 21C reach their peak in late July and August then gradually disappear. In parts of Ontario there are three species of white grubs which infest lawns - European chafer June beetle and Japanese beetle.
Adults emerge from late June into summer. Adults emerge from the soil in late June through mid-July feeding actively in sunny locations for 30-45 days. Adult females lay eggs in moist sod in July.
Where possible homeowners can knock adults into a bucket of soapy water to smother. Japanese beetle life cycle. The most common species is the European.
Dont worry thats the kind in those. Thus for the usual JB pupation window between May 15 and June 15 in Ontario pesticides are likely to be less effective so application during this time should be avoided with careful planning. Our female JBs begin laying her eggs in July.
June Beetle June beetles emerge from the soil during the latter part of May and early June and fly in. Beetles emerge from the soil in late June or early July begin flying when the temperature is about 21C reach their peak in late July and August then gradually disappear. Timing Nematode Treatments to JB Life Cycle July to September.
Economic injury by Japanese beetles is. Japanese Beetle Popillia japonica adults are starting to take flight in southern Ontario. Within the next 20 days the first instar molts to form the second instar.
There is only one generation per year. Adults emerge in spring around the same time as Japanese beetles. Grubs will grow in length as they feed and mature.
Spring early summer. Females excavate soil cavities several inches deep for their eggs which they lay in masses. Consult the life cycle chart for timing or visit the Iowa State University website for some good life cycle information.
June Beele and Japanese Beetle Life Cycle Text equivalent of Figure 7. The Japanese beetle apparently will feed on about 300 plant species. Eggs hatch within a week or two and tiny grubs emerge.
Japanese grubs unlike June bugs are highly active during the. Japanese beetle larvae have a V-shaped series of bristles on their raster the underside of the tip of the abdomen. In most parts of its range the Japanese beetle life cycle takes just a year but in northern areas it may stretch to two years.
This is easily recognizable by the white dots eggs often on the Japanese beetles thorax. Japanese beetles also produce grubs in their juvenile phase which can be controlled in much the same way as common white grubs. The adults are very active for about six to eight weeks emerging in late June or early July and reaching their peak in late July and August.
The Life Cycle of a June Bug. The egg is laid by the female Asian longhorned beetle in a notch that she chews into the bark of a tree. Up to 25-30 cm.
One female will lay eggs at multiple sites with the possibility of a single beetle laying up to 100 eggs. Japanese beetles cause leaves to appear skeletonized. They have been spotted in Hamilton and Toronto this week.
This cycle is repeated until the female lays 40 to 60 eggs. Japanese Beetle Life Cycle. Summer beetles lay eggs primarily in turf.
Within 46 weeks of breaking hibernation the larvae will pupate. Adults feed on leaf material above ground using pheromones to attract other beetles and overwhelm plants skeletonizing leaves from the top of the plant downward. Injury and Management This beetle has a large and diverse host range including woody trees such as elms to annual crops such as corn and soybean and even golf course greens.
Their life cycle is one generation a year. They are in different stages during their life cycle. After burrowing the female beetle then lays a single egg.
Midsummer the eggs hatch and the young grubs begin to feed. Japanese Beetle Life Cycle. They feed on foliage and mate during the day.
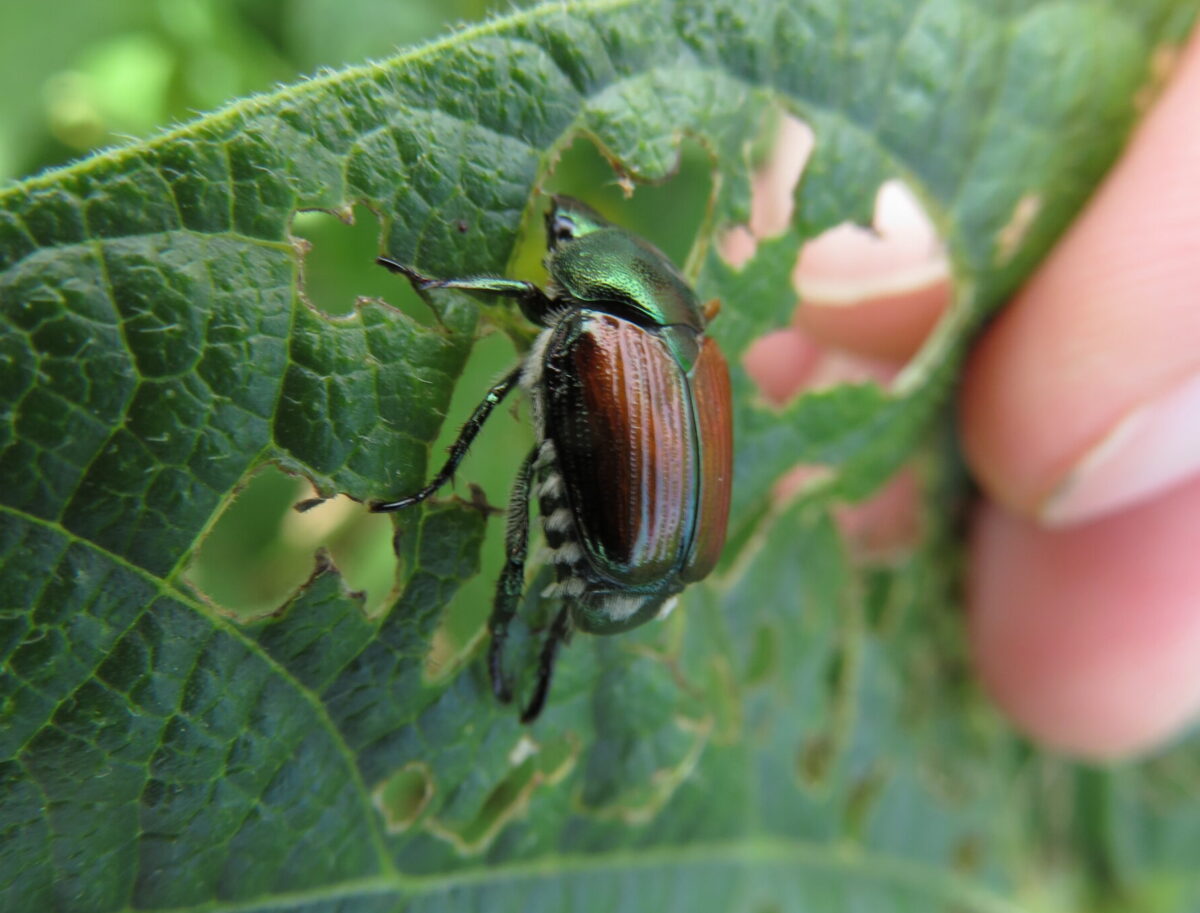

Japanese Beetle Dry Bean Agronomy

How To Identify Soldier Beetles What Are Soldier Beetles Good For In Gardens Garden Pests Garden Bugs Garden Insects

Dung Beetle Life Cycle Clipart Set Download Commercial Graphics By Clipart 4 School Https Clipart4school Com Product Dung B Clip Art Life Cycles Beetle
Japanese Beetles In The Urban Landscape
Japanese Beetles In Nursery And Turf

Harmonia Axyridis Ladybug Ladybug Life Cycle Ladybird
Japanese Beetle Management In Minnesota
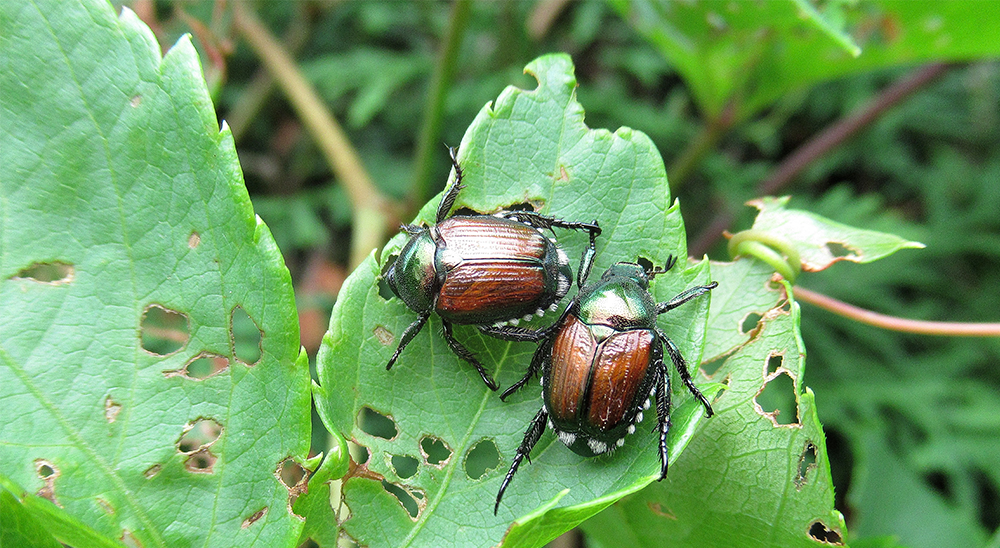

Controlling Japanese Beetles Aphids Ants And Caterpillars Royal City Nursery

Ladybug Lady Beetle Larvae Identification Walter Reeves The Georgia Gardener Lady Beetle Beetle Larvae
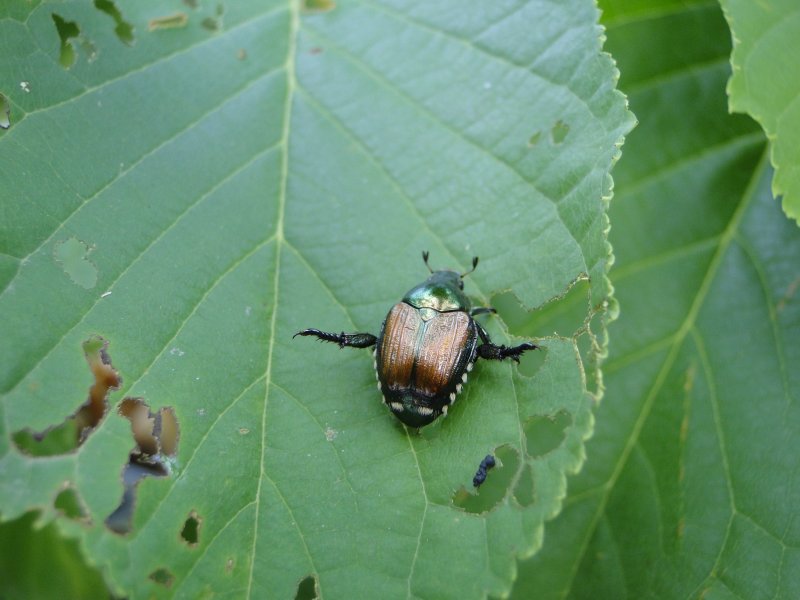

Japanese Beetle In Nebraska Nebraska Forest Service

Japanese Beetles Coming Soon To A Plant Near You Fight Back
Life Cycle Of The Japanese Beetle Including A Eggs David Cappaert Download Scientific Diagram

Japanese Beetles Coming Soon To A Plant Near You Fight Back
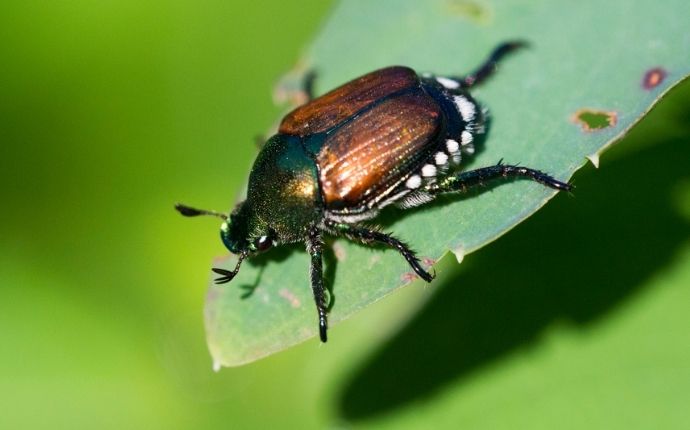

What Do June Bugs Eat Learn Their Diet Life Cycle And How To Stop Them

Japanese Beetle Life Cycle Youtube



